VISIBILITY STANDARDS CHANGED
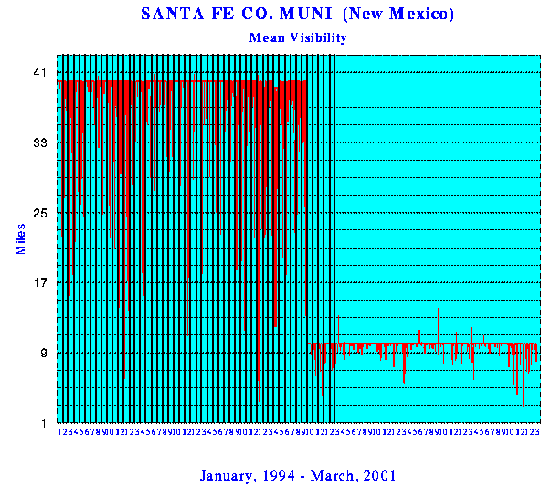
The United States National Climatic Data Center, National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, changed their visibility reporting methods, as well as data results, from a maximum 40 miles to a limit of 10 miles. It is of question why this change was made, and whether it is related to the increasing numbers of aerosol observations. Graphs are shown for the period January 1994 to March 2001 for Santa Fe, New Mexico, showing not only the changes to the reporting standards, but also if is seen that the number of days of visibility under 10 miles is substantially increased.